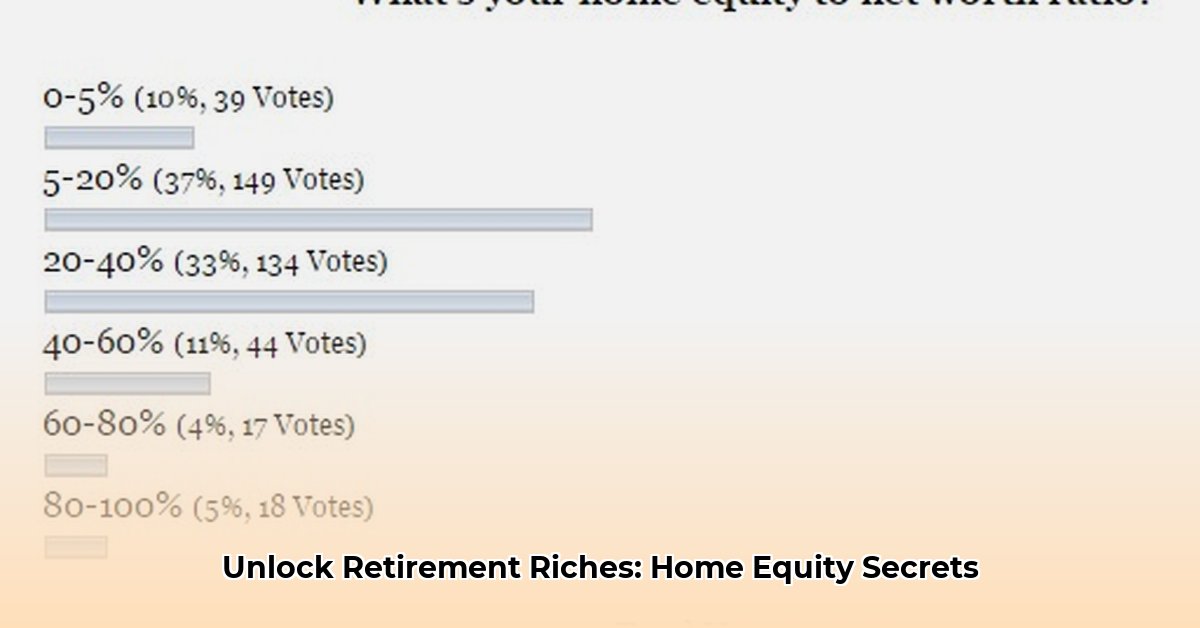
How Much Should Your Home Be of Your Net Worth?
Figuring out the right balance of your wealth tied up in your home is crucial for a secure retirement. There's no one-size-fits-all answer; it depends entirely on your unique circumstances and life stage. Let's explore how to make this important financial decision.
Key Takeaway: The ideal percentage of your net worth in your home isn't fixed; it changes based on your risk tolerance, time horizon, market conditions, and retirement planning. This guide will help you find the right balance for your situation.
Debunking the "20-30% Rule" – It's a Guideline, Not a Law
You've likely heard the 20-30% rule – that your home shouldn't exceed 20-30% of your total net worth. While this serves as a useful starting point, it's not universally applicable. A young couple might comfortably handle a higher percentage, while someone nearing retirement would benefit from a lower one to maintain liquidity.
Quantifiable Fact: The appropriate percentage varies greatly, depending on factors like age, financial goals, and risk tolerance. What's right for a 30-year-old might be risky for a 60-year-old.
Key Factors Influencing Your Home Equity Percentage
Several factors influence the ideal home equity percentage for you:
- Risk Tolerance: Are you comfortable with potential home value fluctuations? Higher risk tolerance might mean a higher percentage.
- Time Horizon: Planning for early retirement? You'll likely need more liquid assets, suggesting a lower percentage in your home.
- Housing Market Conditions: A booming market might justify a higher percentage, but a downturn necessitates caution.
- Retirement Plan Status: Are you on track for comfortable retirement? A solid plan might allow for a higher percentage.
- Emergency Fund: A substantial emergency fund provides flexibility to handle unexpected expenses, potentially allowing for a higher home equity percentage.
- Debt Levels: High debt necessitates a lower home equity percentage to ensure financial stability.
Home Equity Percentages Across Life Stages
This table illustrates how the ideal home equity percentage may change throughout your life:
| Life Stage | Home Equity Percentage: What to Consider |
|---|---|
| Young Professionals | Higher percentage possible; focus on building equity and leveraging potential price appreciation. |
| Families with Children | Prioritize stability and suitability; percentage may fluctuate based on needs. |
| Pre-Retirement | Gradually reduce percentage, building liquid assets for retirement. |
| Near Retirement | Lower percentage is crucial; prioritize easy access to funds. Downsizing may be beneficial. |
| Retired | Maintain lower percentage; ensure home suits current and future needs. |
Potential Risks of High Home Equity
A significant portion of your net worth tied up in your home exposes you to risks:
- Market Volatility: Home prices fluctuate; a downturn could significantly impact your net worth.
- Liquidity Constraints: Your home isn't easily converted to cash for emergencies.
- Unforeseen Expenses: Unexpected home repairs can drain your finances.
Rhetorical Question: Are you prepared for the potential financial impact of a sudden market downturn on your home's value?
Smart Steps to Manage Your Home Equity
Follow these actionable steps to effectively manage your home equity:
- Regular Reviews: Monitor your net worth and home equity annually (or semi-annually).
- Diversification: Spread your investments across various asset classes (stocks, bonds, etc.).
- Emergency Fund: Maintain a substantial emergency fund (ideally 3-6 months of living expenses).
- Long-Term Vision: Align your home equity with your overall financial goals and retirement plan.
- Professional Advice: Consult a financial advisor for personalized guidance.
Expert Quote: "A well-diversified portfolio, including liquid assets, is essential for mitigating risk and ensuring financial security in retirement," says Dr. Sarah Chen, a certified financial planner at the Institute for Financial Planning.
How to Strategically Downsize My Home Near Retirement
Downsizing near retirement can significantly improve your financial situation, but it requires careful planning. This section outlines a strategic approach to maximize gains and minimize risks.
Understanding Your Home Equity Position
Your home equity (market value minus mortgage balance) is a substantial asset. As retirement approaches, diversifying beyond your home becomes increasingly important to maintain liquidity.
Planning Your Downsizing Strategy
- Accurate Valuation: Obtain multiple professional appraisals to avoid overestimating your home's worth.
- Comprehensive Budgeting: Account for all expenses (realtor fees, closing costs, moving expenses).
- Market Research: Research housing markets in your target areas.
- Financial Projections: Work with a financial advisor to model the impact on your retirement portfolio.
- Tax Planning: Consult a tax professional to minimize capital gains taxes.
Minimizing Risk and Maximizing Gains
| Risk Factor | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|
| Overestimating Sale Price | Get multiple appraisals; stay informed on market trends. |
| Underestimating Costs | Develop a thorough budget including contingency funds. |
| Unfavorable Market Timing | Be flexible with your timeline; monitor market shifts. |
| Emotional Attachment | Accept professional assistance to manage emotional aspects of selling your home. |
| Health-related Issues | Prioritize accessibility and maintainability in your new home. |
Step-by-Step Action Plan
- Assess your financial situation.
- Determine your ideal home size and location.
- Get multiple property valuations.
- Create a detailed budget.
- Consult financial and tax professionals.
- Set a realistic timeline.
- Begin your search for a new home.
- List your current home for sale.
- Complete both sales and purchases.
- Reinvest the proceeds.
By following these steps, you can strategically downsize your home near retirement to optimize your investment portfolio and ensure a secure financial future. Remember to always seek professional financial and tax advice.